Printing Technologies
Exploring the Diverse Methods of Additive Manufacturing
Overview
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, encompasses a variety of technologies, each with its own strengths and applications. This page provides an overview of the primary 3D printing technologies
Each technology offers unique benefits, allowing us to meet a wide range of customer needs, from rapid prototyping to small series production.
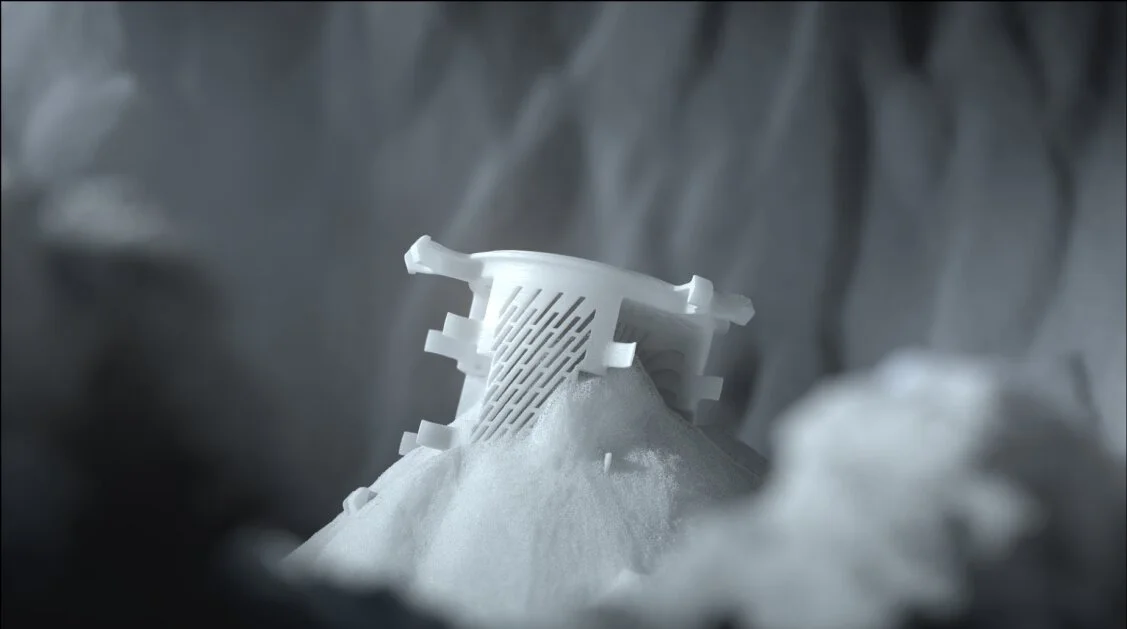
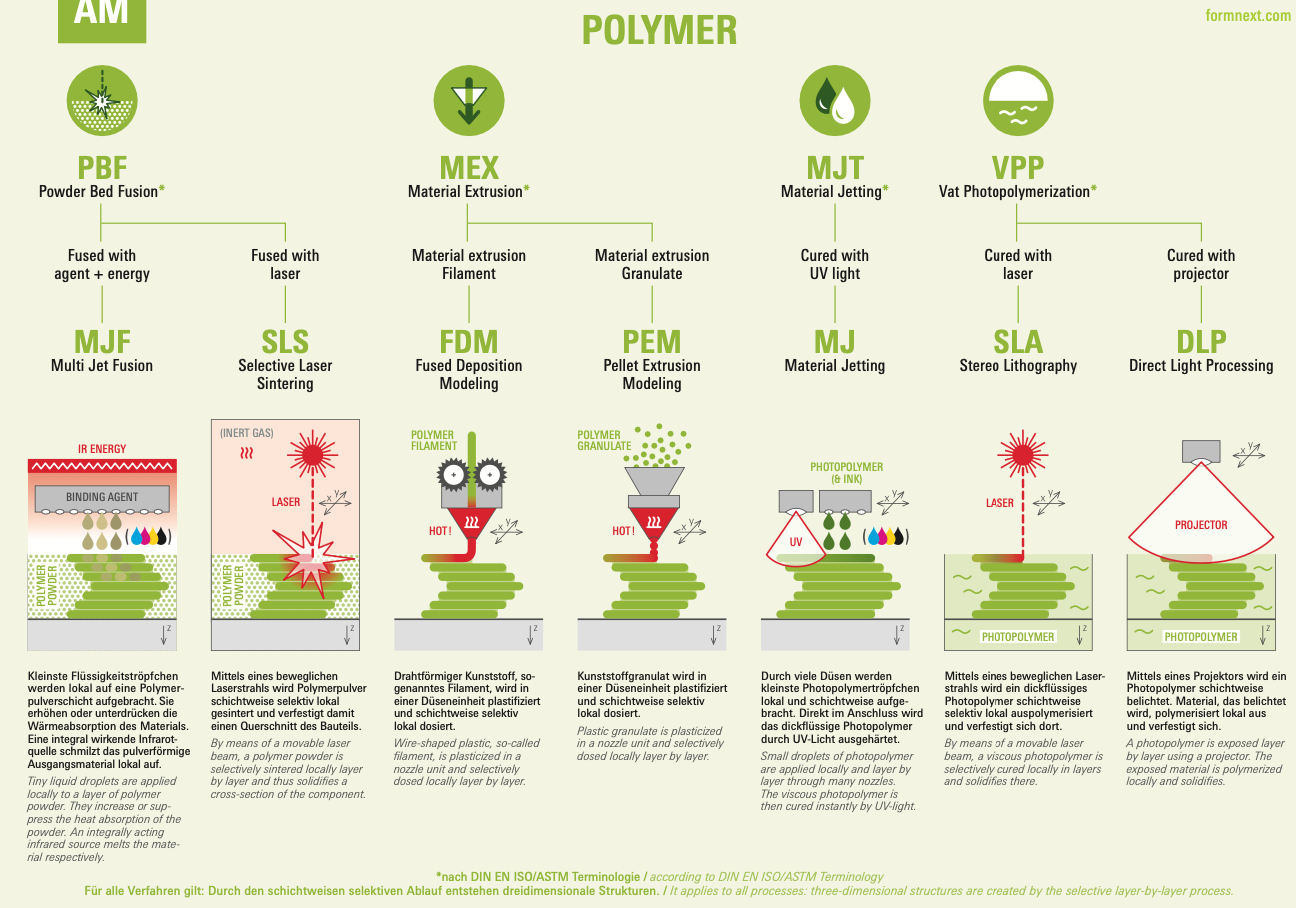
Powder Bed Fusion (PBF)
Powder Bed Fusion is a versatile and widely used 3D printing technology known for its precision and material properties. PBF works by spreading a thin layer of powder and selectively fusing it with energy
Key Technologies:
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Ideal for producing durable, functional parts with excellent mechanical properties. SLS is perfect for both prototyping and end-use applications.
Multi Jet Fusion (MJF): Offers high-speed production with fine detail and uniform mechanical properties. MJF is well-suited for small batch production and functional prototypes.
PBF offers high precision and excellent mechanical properties, making it efficient for small batch production, though it requires post-processing for optimal surface finish.
Material Extrusion (MEX)
Material Extrusion, commonly known as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), is one of the most accessible 3D printing technologies. It involves extruding thermoplastic material layer by layer to build a part.
Key Technologies:
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Known for its cost-effectiveness and ability to create strong, durable parts. FDM is excellent for functional prototypes, custom tools, and low-volume production.
MEX is cost-effective and widely available, producing strong, durable parts ideal for functional prototypes, although it has lower resolution and surface finish compared to other methods.
Vat Photopolymerization (VPP)
Vat Photopolymerization uses a vat of liquid photopolymer resin, which is selectively cured by a light source to form solid layers.
Key Technologies:
Stereolithography (SLA) & Masked Stereolithography (MSLA): Produces high-resolution parts with smooth surface finishes, making it ideal for detailed prototypes and models.
Digital Light Processing (DLP): Similar to SLA but uses a digital light projector screen to flash a single image of each layer, enabling faster print times.
VPP offers high resolution and excellent surface finish, perfect for detailed prototypes, though parts have limited mechanical strength.
Material Jetting (MJ)
Material Jetting deposits droplets of material layer by layer to build parts, known for producing highly detailed and smooth parts.
Key Technologies:
PolyJet: Capable of printing in multiple materials and colors simultaneously, PolyJet creates detailed models with high accuracy.
MJ delivers high detail finishes with multi-material and full-color capabilities, though it has higher material costs and parts may be less durable.
Metal Additive Manufacturing (Metal AM)
Metal Additive Manufacturing uses similar layer-by-layer techniques to produce metal parts, significant in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical.
Key Technologies:
Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
Metal AM produces strong, complex metal parts suitable for high-performance applications, though it involves high costs and complex post-processing.
What are the key differences between PBF, MEX, VPP, MJ and Metal AM technologies?
Which 3D printing technology is best suited for prototypes, complex geometries or small-batch production?
What limitations should I consider when choosing between different 3D printing technologies?
Frequently Asked Questions
Need Help Choosing the Right Technology?
We are here for you!
Why Choose Norra AM?
-

Easy
From the moment you contact us, our streamlined processes and instant quoting system make ordering prototypes straightforward and hassle-free. We simplify the complex, so you can focus on innovation.
-

Fast
Our state-of-the-art manufacturing technology allows us to produce high-quality prototypes with rapid turnaround times. Whether you need a single prototype or a large batch, we deliver your parts quickly to keep your projects on track.
-

Local
Based in Hudiksvall, we provide personalized support and fast delivery times. Being local means we understand your needs better and can offer timely assistance and services, ensuring your prototypes meet your exact specifications.